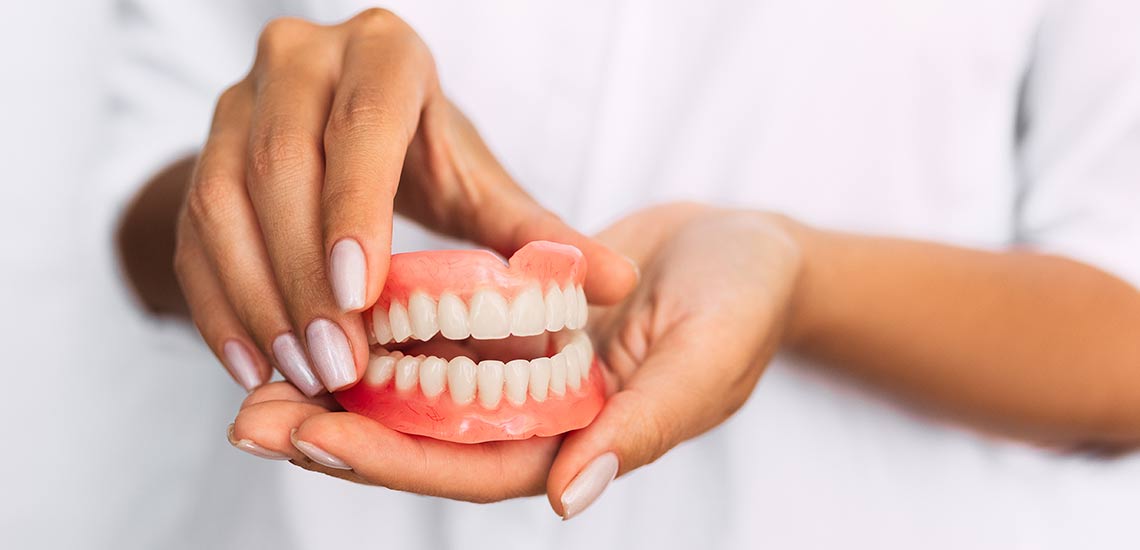
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, and are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants (fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they are used to replace missing teeth on the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch.
Medical uses of Dentures
Dentures do not feel like real teeth and may take some time to get used to. Require brush and plaque removal like your real teeth.
Dentures can help people through:
Mastication or chewing ability is improved by replacing edentulous areas with denture teeth.
Aesthetics, because the presence of teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance that results from the loss of teeth.
Pronunciation, because replacing missing teeth, especially the anteriors, enables patients to speak better. There is especially improvement in pronouncing words containing sibilants or fricatives.
Self-esteem, because improved looks and speech boost confidence in the ability to interact socially.
Complications
Stomatitis
Denture stomatitis is an inflammatory condition of the skin under the dentures.It can affect both partial and complete denture wearers, and is most commonly seen on the palatal mucosa. Clinically it appears as simple localized inflammation (Type 1), generalized erythema covering the denture-bearing area (Type II) and inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (Type III). People with denture stomatitis are more likely to have angular cheilitis. Denture stomatitis is caused by a mixed infection of Candida albicans (90%) and a number of bacteria like Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Fusobacterium and Bacteroides species. Acrylic resin is more susceptible for fungal colonisation, adherence and proliferation. Denture trauma, poor denture hygiene and nocturnal denture wear are local risk factors for denture stomatitis. Systemic risk factors for denture stomatitis include nutritional deficiencies, immunosuppression, smoking, diabetes, use of steroid inhaler and xerostomia. A person should be investigated for any underlying systemic disease. Improve the fit of ill-fitting dentures to eliminate any dental trauma. Stress on the importance of good denture hygiene including cleaning of the denture, soaking the dentures in disinfectant solution and not wearing it during sleeping at night is the key to treat all types of denture stomatitis. Topical application and systemic use of antifungal agents can be used to treat denture stomatitis cases that fail to respond to local conservative measures.
Ulceration
Mouth ulceration is the most common lesions in people with dentures. It can be caused by repetitive minor trauma like poorly fitting dentures including over-extension of a denture. Pressure indicating paste can used to check the fitting of dentures It allows the areas of premature contact to be distinguished from areas of physiologic tissue contact.Therefore, the particular area can be polished with acrylic bur. Leaching of residual monomer methylmethacrylate from inadequately cured denture acrylic resin material can cause mucosal irritation and hence oral ulceration as well. Advise the person to use warm salt water mouth rinses and a betamethasone rinse can heal ulcer.[6] Review of persisting oral ulcerations for more than 3 weeks is recommended.
Tooth loss
People can become entirely edentulous (without teeth) for many reasons, the most prevalent being removal due to dental disease, which typically relates to oral flora control, i.e., periodontal disease and tooth decay. Other reasons include pregnancy, tooth developmental defects caused by severe malnutrition, genetic defects such as dentinogenesis imperfecta, trauma, or drug use.
Periodontitis is defined as an inflammatory lesion mediated by host-pathogen interaction that results in the loss of connective tissue fibre attachment to the root surface and ultimately to the alveolar bone. It is the loss of connective tissue to the root surface that leads to teeth falling out. The hormones associated with pregnancy increases the risk of Gingivitis and vomiting.
Hormones released during pregnancy softens the cardia muscle ring that keeps food within the stomach. Hydrochloric acid is the acid involved in gastric reflux, also known as morning sickness. This acid, at a pH of 1.5-3.5 coats the enamel on the teeth; at a pH of 6.5 and mainly affect the palatal surfaces of the maxillary teeth, eventually the enamel is softened and easily wears away.
Dental trauma refers to trauma (injury) to the teeth and/or periodontium (gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone). Strong force may cause the root of the tooth to completely dislocate from its socket, mild trauma may cause the tooth to chip.
Types of Dentures
Removable partial dentures
Removable partial dentures are for patients who are missing some of their teeth on a particular arch. Fixed partial dentures, also known as "crown and bridge" dentures, are made from crowns that are fitted on the remaining teeth. They act as abutments and pontics and are made from materials resembling the missing teeth. Fixed bridges are more expensive than removable appliances but are more stable.
Another option in this category is the flexible partial, which takes advantage of innovations in digital technology. Flexible partial fabrication involves only non-invasive procedures. Dentures can be difficult to clean and can affect oral hygiene.
Complete dentures
Complete dentures are worn by patients who are missing all of the teeth in a single arch—i.e., the maxillary (upper) or mandibular (lower) arch—or, more commonly, in both arches.
Copy dentures
Can be made for either partial but mainly complete denture patients. These dentures require fewer visits to make and usually are made for older patients, patients who would have difficulty adjusting to new dentures, would like a spare pair of dentures or like the aesthetics of their dentures already. This requires taking an impression of the patients current denture and remaking them.
Materials of Dentures
Dentures are mainly made from acrylic due to the ease of material manipulation and likeness to intra-oral tissues, i.e. gums. Most dentures made are fabricated from heat-cured acrylic polymethyl methacrylate and rubber-reinforced polymethyl methacrylate. Coloring agents and synthetic fibers are added to obtain the tissue-like shade, and to mimic the small capillaries of the oral mucosa, respectively. However, dentures made from acrylic can be fragile and fracture easily if the patient has trouble adapting neuromuscular control. This can be overcome by reinforcing the denture base with cobalt chromium (Co-Cr). They are often thinner (therefore more comfortable) and stronger (to prevent repeating fractures).